Cloud storage can be eco-friendly - and it’s not just about saving the planet. Businesses can cut carbon emissions by up to 99%, improve energy efficiency by 93%, and even save on costs with greener cloud options. Providers like AWS, Google, and Microsoft are leading with renewable energy, advanced cooling systems, and AI-driven optimizations.
Key Takeaways:
- Energy Efficiency: Cloud infrastructure is up to 4.1x more efficient than on-premises systems.
- Renewable Energy: Top providers use 100% clean energy, reducing emissions.
- Cost Savings: Efficient systems lower energy use and operational costs.
- Compliance: Tools simplify emissions reporting for new regulations like the EU’s CSRD.
Switching to eco-friendly cloud storage isn’t just a smart environmental choice - it’s a business advantage. Start by analyzing your current storage, choose a green provider, and monitor usage to maximize efficiency.
Greening the Cloud: Engineering for a Sustainable Digital Future
Technologies Behind Eco-Friendly Cloud Storage
The push for greener cloud storage is powered by advancements in technology aimed at reducing energy use. Three standout innovations are leading this charge: energy-efficient infrastructure, modern cooling systems, and AI-driven optimization. Together, these breakthroughs help data centers lower their environmental footprint while keeping performance levels high. Let’s take a closer look at how each of these technologies contributes to sustainable cloud storage.
Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
Cloud providers are ditching traditional, power-hungry processors in favor of chips designed with energy efficiency in mind. Take AWS Graviton-based instances, for example - they consume up to 60% less energy compared to standard EC2 instances. Similarly, Google’s sixth-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), called Trillium, is 67% more energy-efficient than its earlier version.
Energy savings also extend to storage. Solid State Drives (SSDs) use significantly less power than traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), and LTO tape technology offers an energy-saving solution for archival data by requiring no power when idle. Shifting inactive data from HDDs to LTO tape can cut CO₂ emissions by a staggering 6.5 times. Additionally, server virtualization enables multiple virtual machines to share a single physical server, consolidating workloads and cutting down on the number of devices that need power and cooling.
These hardware improvements create a strong foundation for further energy reductions, especially when combined with advanced cooling technologies.
Cooling Technologies
Cooling systems can account for as much as 40% of a data center's energy use. To combat this, many providers are adopting more efficient methods. Liquid cooling systems, including cold plates and immersion cooling, are gaining traction because liquids are far better at transferring heat than air. This shift can reduce a data center's total energy consumption by 15% to 20%.
In 2024, AWS introduced a flexible cooling solution for its Trainium3 AI chips, which cut mechanical energy use by 46% during peak cooling periods. Meanwhile, Microsoft rolled out a liquid heat exchanger in 2025, enabling traditional air-cooled data centers to handle high-density AI workloads without relying on water evaporation. Other natural cooling methods, such as geothermal and free-air cooling, take advantage of ambient temperatures, while solar-powered cooling systems use renewable energy to directly power cooling infrastructure .
But the innovation doesn’t stop with hardware - AI is taking energy optimization to the next level.
AI and Machine Learning for Optimization
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing energy efficiency in data centers. In 2024, AWS implemented generative AI software to determine the most energy-efficient server arrangements within its facilities. This initiative helped AWS achieve a global Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) of 1.15, which is 12% better than the public cloud industry average.
AI also fine-tunes cooling systems in real time. By analyzing input from thousands of sensors, AI tools can adjust cooling levels instantly to match workload demands, cutting cooling electricity use by 25%. Google has reported impressive results, with its data centers being 1.8 times more energy-efficient than typical enterprise facilities. Thanks to AI-driven optimization, Google maintains an average annual PUE of just 1.10.
"Artificial intelligence is changing every sector of society, but its rapid growth comes with a real footprint in energy, water and carbon." – Fengqi You, Professor in Energy Systems Engineering, Cornell Engineering
How to Evaluate Cloud Storage Providers
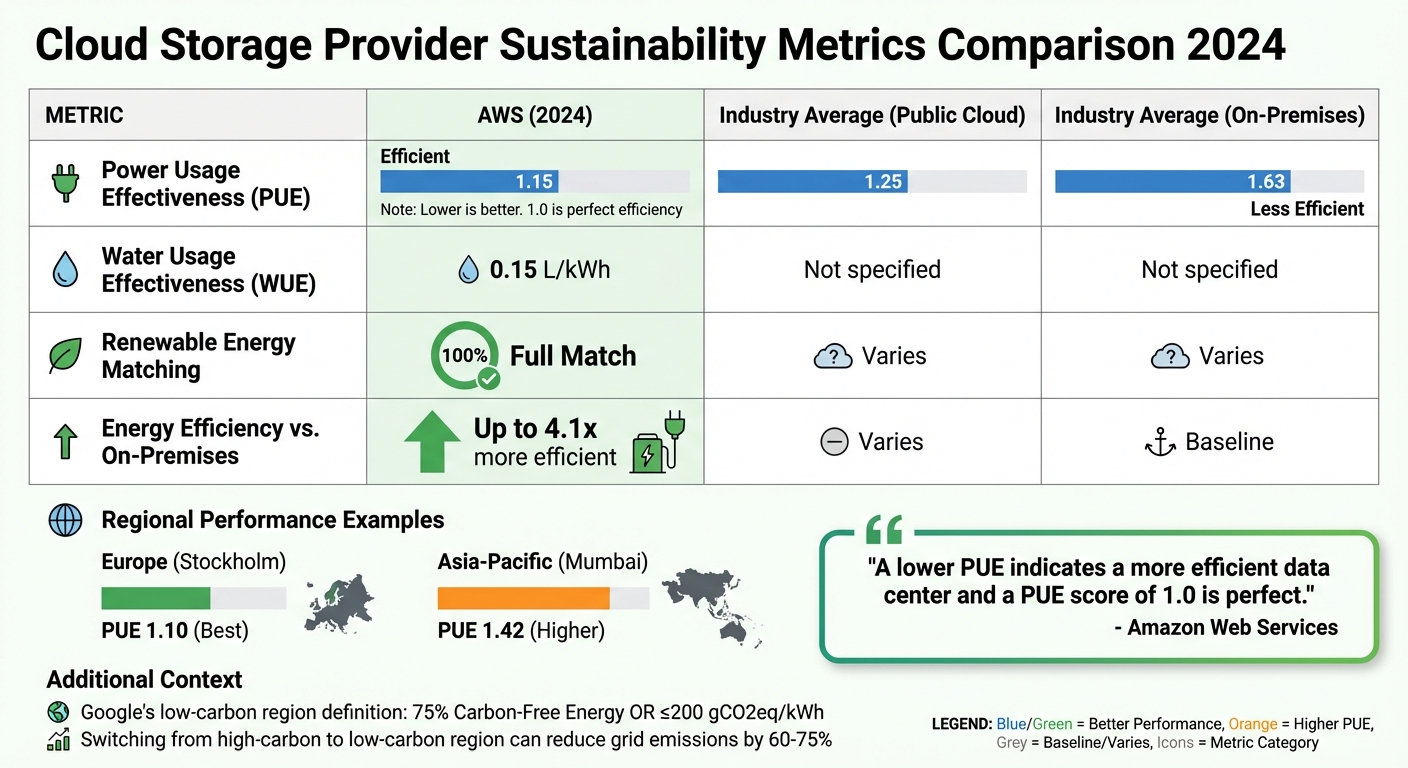
Cloud Storage Provider Sustainability Metrics Comparison 2024
When choosing a cloud storage provider, it's essential to assess their energy efficiency, use of renewable resources, and transparency regarding environmental practices. Some providers are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional on-premises setups - up to 4.1 times more efficient - while others might rely on carbon offsets instead of directly utilizing renewable energy sources.
Key Features to Look For
A good starting point is Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE), which measures how efficiently a data center consumes energy. A lower PUE score indicates better energy efficiency. For example, in 2024, AWS reported a global PUE of 1.15, outperforming the industry average of 1.25 for public clouds and 1.63 for on-premises data centers.
"A lower PUE indicates a more efficient data center and a PUE score of 1.0 is perfect." – Amazon Web Services
Regional variations are also worth noting. AWS Europe (Stockholm) achieved a PUE of 1.10, while AWS Asia-Pacific (Mumbai) reported a higher PUE of 1.42.
Renewable energy sourcing is another critical factor. Ensure the provider uses 100% renewable electricity instead of relying on carbon offsets. Claims should be backed by Energy Attribute Certificates, such as Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) or Guarantees of Origin.
Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) is particularly important in areas prone to water scarcity. AWS reported a global WUE of 0.15 liters per kilowatt-hour (L/kWh) in 2024, a 17% improvement over the previous year and a 40% improvement since 2021.
Transparency about Scope 3 emissions is increasingly important. While many providers disclose Scope 1 (direct emissions) and Scope 2 (indirect emissions from purchased electricity), Scope 3 accounts for emissions across the entire value chain, including manufacturing and construction. AWS, for instance, reduced embodied carbon in 2024 by building 38 data centers with lower-carbon concrete and 36 with lower-carbon steel.
Look for independent verification through third-party certifications. In 2024, AWS received an EcoVadis score of 73, placing it in the top 15% of its industry. Additionally, AWS was recognized as a "Leader" in the 2025 IDC MarketScape for Worldwide Sustainable Cloud Datacenter Vendor Assessment.
Lastly, consider circular economy practices. In 2024, AWS's re:Cycle Reverse Logistics hubs sold 11.5 million components in the secondary market and sourced 16% of spare parts from reused inventory, helping to avoid an estimated 110,000 tons of carbon emissions.
These metrics provide a solid foundation for comparing cloud providers.
Provider Comparison
To further simplify your evaluation, here’s a comparison of key sustainability metrics across providers:
| Metric | AWS (2024) | Industry Average (Public Cloud) | Industry Average (On-Premises) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) | 1.15 | 1.25 | 1.63 |
| Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) | 0.15 L/kWh | Not specified | Not specified |
| Renewable Energy Matching | 100% | Varies | Varies |
| Energy Efficiency vs. On-Premises | Up to 4.1x more efficient | Varies | Baseline |
Regional performance can vary widely based on local grid carbon intensity and the availability of renewable energy. For example, Google defines a "low carbon" region as one with at least 75% Carbon-Free Energy (CFE) or a grid carbon intensity of no more than 200 gCO2eq/kWh. Tools like region pickers can help you identify data centers with the lowest environmental impact. Switching from a high-carbon to a low-carbon region can reduce grid emissions by 60–75%.
Finally, examine both location-based and market-based reporting. Providers should offer customer-specific dashboards that detail your carbon footprint and help track your progress toward sustainability goals.
sbb-itb-01010c0
How to Implement Eco-Friendly Cloud Storage
Switching to eco-friendly cloud storage means understanding your current impact, carefully planning your migration, and continuously optimizing your usage. The process relies on a shared responsibility model: cloud providers manage infrastructure, power, and cooling (sustainability of the cloud), while you focus on optimizing workloads and resources (sustainability in the cloud).
Assess Your Current Storage Needs
Start by analyzing your existing infrastructure using tools like AWS Cost and Usage Reports, GCP Billing Export, or Azure Consumption Management. These tools provide detailed insights into resource consumption, including compute, storage, and networking. Break down usage into units like byte-seconds or GB-months to account for the different energy profiles of HDDs and SSDs.
Keep in mind that energy use is often tied to allocated capacity rather than actual storage due to over-provisioning. Factor in replication overhead and use cloud-native analytics to identify and eliminate "dark data" - unused or redundant data that consumes energy unnecessarily.
Also, consider where your data is stored. The carbon intensity of electricity grids varies significantly by region.
"A data center running off mostly coal and natural gas that is 10 times as energy efficient will still produce far more emissions than one powered entirely by solar or wind." – Climate Primer
With a clear picture of your storage footprint, you can identify providers offering renewable energy-backed solutions.
Migrate to Green Providers
Once you've assessed your needs, the next step is migrating to providers committed to renewable energy. Look for regions with cleaner energy grids, such as Oregon, Finland, or Ireland, which are known for their renewable energy availability. For example, in 2024, AIA Sri Lanka moved its on-premises data center to Microsoft Azure under CTO Umeshi de Fonseka's leadership. This shift not only reduced their carbon footprint but also cut costs by 20%.
During migration, enable features like Object Lifecycle Management (OLM) or "Autoclass." These tools automatically move data to lower-cost, energy-efficient storage classes based on usage patterns. Storing infrequently accessed data in "colder" classes - like Nearline, Coldline, or Archive - can significantly reduce the energy required for immediate availability. A great example of this is Vimeo, which transitioned its video upload infrastructure to Google Cloud Storage in 2024. By leveraging multi-regional buckets and resumable upload capabilities, they reduced backend hardware management and improved efficiency.
While your provider handles the sustainability of the cloud, your role is to ensure your resource usage aligns with sustainability goals.
Monitor and Optimize Usage
After migrating, ongoing monitoring is key to maintaining and improving efficiency. Use dashboards provided by your cloud provider to track Scope 3 emissions and identify areas for optimization. Automated lifecycle management tools can help minimize idle energy use by ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
Pay attention to idle versus active power usage to avoid over-provisioning. Use metrics like Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) to align with industry standards. Additionally, consider both location-based and market-based reporting. Location-based reporting reflects the actual energy grid mix, which is helpful for operational decisions, while market-based reporting accounts for renewable energy contracts, aiding in corporate greenhouse gas inventories.
Set clear sustainability metrics - such as greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption - and track your progress monthly to stay on course.
Business Benefits of Eco-Friendly Cloud Storage
Eco-friendly cloud storage isn't just good for the planet - it offers real advantages for businesses. From cutting costs to enhancing your reputation and staying ahead of regulations, making the switch can deliver measurable results.
Cost Savings Through Energy Efficiency
Switching to energy-efficient cloud infrastructure can significantly lower operational expenses. For instance, moving workloads to Microsoft Azure can improve energy efficiency by up to 93% compared to traditional on-premises systems. That’s a substantial saving for businesses looking to trim their energy bills.
Cloud technologies also play a key role in reducing decarbonization costs, cutting them by 2–10%, and they can lower energy use by up to 10% through tools like digital twins and machine learning models. Automated sustainability reporting tools save even more, slashing reporting costs and time by as much as 70%.
"Using cloud-powered technologies can reduce the cost of implementing a decarbonization initiative by 2 to 10 percent." – McKinsey
Beyond cost savings, these efficiencies contribute to building trust and credibility with stakeholders. Companies that lead in sustainability often enjoy lower borrowing costs and better equity market performance.
Enhance Your Brand Reputation
Sustainability is no longer optional - it’s a priority for customers, investors, and employees. By adopting eco-friendly cloud storage, businesses can demonstrate a genuine commitment to environmental responsibility. Tools like Azure's Emissions Impact Dashboard provide transparency, enabling companies to share reliable data with stakeholders.
A green approach to business doesn’t just improve public perception; it also attracts top talent. Today’s workforce increasingly values employers who prioritize environmental stewardship. For example, AWS received a Silver Medal from EcoVadis in 2024, scoring 73 out of 100 and ranking in the 93rd percentile within the data processing and hosting industry.
Strong environmental practices don’t just enhance your reputation - they also position your company to thrive in increasingly regulated markets.
Stay Ahead of Environmental Regulations
Eco-friendly cloud storage can help businesses meet evolving environmental standards and avoid costly penalties. With regulations like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) imposing fines of up to €10 million for non-compliance, staying ahead is crucial. Built-in compliance tools and automated reporting features make it easier to adapt to these demands.
Cloud-enabled platforms also improve data transparency, which is essential for tracking Scope 3 emissions - a growing focus in regulatory frameworks. For businesses with complex supply chains, this transparency simplifies compliance and planning. In fact, cloud-based data observability can cut the time to develop a decarbonization strategy from 6–8 weeks down to just 1 week.
Conclusion
Choosing eco-friendly cloud storage isn't just about ticking off an environmental box - it’s a smart business move with tangible benefits. Green cloud providers can reduce carbon emissions by up to 99% while offering infrastructure that's up to 4.1 times more energy efficient. These efficiencies translate into significant savings, with annual benefits reaching around $86,500 per petabyte of data stored.
To get started, evaluate your current storage needs and environmental impact using tools like the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool or the Azure Emissions Impact Dashboard. Opt for providers committed to renewable energy and consider data center locations powered by cleaner grids. For instance, moving from a high-carbon region like Ohio to Oregon could slash grid emissions by 60% to 75%. Additionally, implement lifecycle policies to shift less frequently accessed data to lower-energy storage tiers and use AI-driven tools to minimize waste.
The importance of renewable energy sources can't be overstated. Even the most efficient data centers relying on fossil fuels produce significantly more emissions than those powered by clean energy. This makes your choice of provider and region crucial for achieving real environmental impact.
Beyond cutting costs, prioritizing sustainability enhances your brand’s reputation and positions your company for long-term success. With major players like Amazon set to match 100% of their global electricity use with renewable energy by 2024, the infrastructure is already in place to support your transition. This approach not only aligns with regulatory and financial objectives but also strengthens your competitive position.
Every step you take, from optimizing workloads to carefully selecting regions, contributes to both profitability and sustainability. Start small, track your progress, and expand your green initiatives as you see results. The time to act is now - lead the way in building a sustainable and competitive future.
FAQs
How can businesses evaluate the environmental impact of their cloud storage?
To get a handle on the environmental impact of your cloud storage, begin by checking the usage metrics your cloud provider offers. These stats can help you estimate both energy consumption and CO₂ emissions using tools that account for electricity emission rates specific to your location. Providers like Google Cloud and AWS often include built-in sustainability insights, making it easier for businesses to gauge their carbon footprint. For more detailed assessments, frameworks like Cloud Carbon Footprint can be incredibly helpful. By digging into these metrics, companies can spot ways to streamline their storage usage and lower their environmental impact.
What are the main advantages of using AI to optimize cloud storage?
Using AI in cloud storage comes with some major perks. For starters, it can cut costs by automating tasks like data management and tiering. This ensures your data is stored in the most budget-friendly way possible.
Another plus? AI boosts energy efficiency, which not only saves resources but also supports eco-friendly initiatives by reducing overall energy use.
On top of that, AI strengthens system performance and reliability, making cloud storage more dependable and responsive. It also offers valuable insights that help businesses make smarter decisions about resource allocation, striking a balance between operational needs and environmental considerations.
How do cooling technologies make cloud storage more eco-friendly?
Cooling systems are a key part of making cloud storage more environmentally friendly, as they help manage the heat generated by servers while cutting down on energy use. Modern data centers now rely on advanced cooling technologies like liquid cooling and optimized airflow. These approaches not only lower energy consumption but also enhance overall performance. For instance, liquid cooling systems can efficiently dissipate waste heat, allowing for more compute power per watt.
In addition to liquid cooling, methods like water-based cooling and evaporative systems are becoming more popular. These techniques consume far less energy than traditional air-conditioning systems and can dramatically reduce both electricity and water usage. Research highlights that swapping out compressor-based cooling systems for these alternatives can slash energy use by up to 20% and decrease water consumption by 36%, all while keeping servers at safe operating temperatures.
For businesses looking to make their cloud storage solutions more eco-friendly, The B2B Ecosystem provides valuable tools and expert guidance. These resources help companies assess cooling options, boost energy efficiency, and incorporate sustainable designs into their cloud strategies. This makes it easier to transition to greener storage solutions while staying aligned with environmental objectives.


