Deploying 5G networks offers faster speeds and greater connectivity but comes with serious risks. Key concerns include vulnerabilities in policies, supply chains, and network architecture. Here’s what you need to know:
- Supply Chain Risks: Counterfeit parts, malware, and manufacturing flaws are common threats. Regular vendor assessments and strict contracts with clear security expectations are essential.
- Infrastructure Readiness: Conduct site surveys, update legacy systems, and test physical and network connections to ensure smooth deployment.
- Network Monitoring: Use continuous monitoring tools, map devices, and implement anomaly detection to secure cloud-native 5G functions.
- Zero Trust Security: Eliminate implicit trust by verifying every user, device, and workload. Use machine learning for threat detection and enforce strict access controls.
- Expert Guidance: Partner with advisors and use AI tools to identify risks, evaluate vendors, and secure your deployment.
5G Deployment Risk Mitigation: 5-Step Security Checklist
5G Security Architecture with Mitigation Strategy (Part 2)
sbb-itb-01010c0
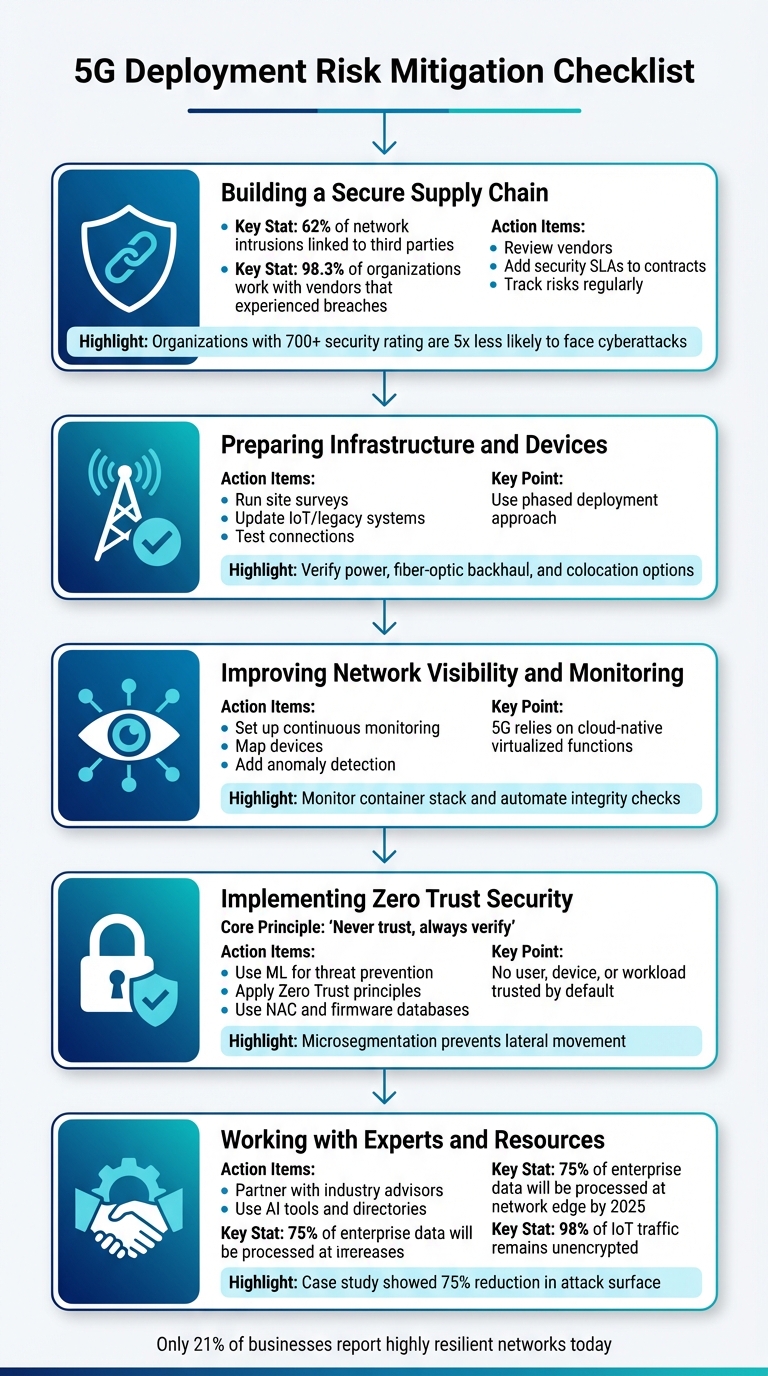
1. Building a Secure Supply Chain
Securing every part of your 5G supply chain is essential. With 62% of network intrusions linked to third parties and 98.3% of organizations worldwide working with vendors that experienced a data breach in the past two years, the stakes couldn't be higher.
1.1. Review and Assess All Vendors
Start by taking stock of every device, component, and vendor involved in your supply chain - this includes hardware, software, and service providers. Use risk scorecards, whether numeric or color-coded, to evaluate vendors based on their financial health, security protocols, certifications, and overall resilience.
Pay extra attention to critical suppliers, as their failure could have the most significant operational consequences. Use questionnaires to dig into their encryption practices, access controls, facility security, and how they vet their personnel. Certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2 are good indicators of adherence to global security standards. Interestingly, organizations with a security rating of 700 or higher are nearly 5 times less likely to face a cyberattack compared to those rated 500 or below.
Once you've completed your evaluations, ensure vendors meet strict security requirements outlined in their contracts.
1.2. Add Security Requirements to Vendor Contracts
Vendor contracts should clearly spell out 5G-specific security expectations. As Ironclad explains:
The purpose of a vendor contract is to allow all parties involved to understand what is expected... and the consequences if those expectations are not met.
Include cybersecurity Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that set measurable security benchmarks. These should cover technical requirements like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), data encryption protocols, and backup systems. Also, outline mandatory incident reporting rules - vendors must notify you promptly about any cyber incidents or vulnerabilities. Add termination clauses to give you a legal way out if a vendor's risk profile becomes unacceptable or they fail to meet their obligations.
Pair these contracts with regular risk reviews to ensure security standards are upheld over time.
1.3. Track Supply Chain Risks Regularly
Maintaining 5G security requires ongoing vigilance. Use continuous monitoring tools to identify new threats and ensure mitigation strategies are effective. Map out dependencies and categorize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact.
Assign specific risk owners and set deadlines for regular reviews. Automated tools can help you assess vendor security in real time, reducing reliance on self-reported data. Look at a wide range of factors, such as financial stability, geopolitical risks, and exposure to natural disasters. To minimize disruptions, diversify your suppliers for critical components, creating redundancies that protect you if one vendor falters.
2. Preparing Infrastructure and Devices for 5G
Once you’ve secured a reliable supply chain, it’s time to ensure your infrastructure and devices are ready to handle the demands of 5G. This process requires careful planning and a structured approach. Start with a phased deployment - test in a single unit before rolling it out across your organization. This method helps identify potential compatibility issues early on and highlights quick successes that can build internal support. Additionally, validate every component, from site conditions to system integrations, to ensure a smooth rollout.
2.1. Run Site Surveys and Compatibility Checks
Site surveys are the backbone of a successful 5G deployment. These surveys help evaluate key factors like zoning, physical site conditions (topography, climate), and environmental considerations to ensure the network performs at its best. Also, verify the availability of sufficient power and fiber-optic backhaul at each site.
Another strategy to consider is colocation, where multiple operators share the same tower. This not only cuts down on redundant construction costs but also accelerates deployment timelines. As Team Boingo emphasizes:
Selecting the right tower operator is just as important as the physical infrastructure itself.
Working with tower operators who already have agreements with major carriers like AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile can significantly reduce deployment times, making the process more efficient.
2.2. Update IoT and Legacy Systems
Before diving into upgrades, take stock of your existing IoT and legacy systems. Identify which components are critical and which can be retired. Involve key departments early in the process to address concerns like uptime, system integration, and data management. Only upgrade systems that could hinder 5G performance - this targeted approach saves time and resources.
2.3. Test Physical and Network Connections
Before going live, put your physical setups and network connections through rigorous testing. Simulate real-world conditions to ensure your infrastructure can handle 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency demands. Tools like AI-RAN can be invaluable here, providing automated performance optimization to fine-tune your network for peak efficiency.
3. Improving Network Visibility and Monitoring
Once your infrastructure is locked down and your devices are thoroughly tested, the next big step is ensuring real-time visibility across your 5G network. Monitoring becomes especially important in 5G environments, which are far more complex than their 4G predecessors. Unlike 4G, 5G relies heavily on cloud-native, virtualized functions, which significantly expand the potential attack surface. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) sums it up well:
5G represents a complete transformation of telecommunication networks, introducing a wealth of benefits that will pave the way for new capabilities.
But with those benefits come fresh risks. The high capacity and low latency of 5G demand robust monitoring to ensure security. This step builds upon your hardened infrastructure, securing your system from the edge all the way to the core.
3.1. Set Up Continuous Monitoring Tools
Start by deploying tools capable of detecting lateral movement within your 5G cloud. In these virtualized environments, a single compromised container or virtual network function can quickly snowball into a network-wide breach. Your monitoring tools should prioritize the container stack, which underpins these virtualized functions, ensuring that customer resources remain securely isolated.
Automating integrity checks is another must. Implement systems to automatically verify the integrity of your cloud resources - like container images, templates, and configuration files - to detect unauthorized modifications. This step is critical for preventing attackers from injecting malicious code during routine updates or maintenance. Once continuous monitoring is up and running, shift your focus to mapping your network devices to uncover specific vulnerabilities.
3.2. Map Devices and Find Vulnerabilities
Go beyond traditional network diagrams by creating detailed, real-time maps of your 5G network. Use heatmaps to monitor signal strength, pinpoint access point locations, and identify coverage gaps as they occur. This level of detail is crucial for 5G, which relies on small cells - a far cry from the centralized towers typical of 4G networks. These small cells are often scattered across utility poles, retail buildings, and office complexes, making comprehensive mapping a necessity.
Don’t overlook the risks of legacy system integration. Many 5G deployments are built on top of existing 4G LTE infrastructure, which can carry over vulnerabilities. Your mapping tools should be equipped to spot these inherited risks and address any blind spots created by proprietary vendor interfaces.
3.3. Add Anomaly Detection Systems
Leverage machine learning to analyze behavior across your network. Machine learning-powered anomaly detection can monitor data at rest, in transit, and in process - especially for critical applications like telemedicine, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
Configure these systems to flag unusual activity, such as unauthorized device connections or suspicious behavior within network slices. As Marin Ivezic, a Partner at PwC, points out:
In light of the reality that 5G networks will carry so much of the world's business in real time... it will become the most critical infrastructure of all time.
4. Implementing Zero Trust Security
With monitoring systems actively tracking your 5G network, the next step is to remove any assumptions of implicit trust across your infrastructure. Traditional perimeter-based security models assume that internal systems and users are inherently safe. However, in the 5G era, where cloud-native functions blur these boundaries, that assumption no longer holds. As Palo Alto Networks explains:
"The most fundamental principle of a Zero Trust model is the complete elimination of implicit trust. This means that no user, device, or workload is trusted by default, even if they are already connected to the corporate network."
Zero Trust flips the conventional "trust but verify" approach on its head, adopting a "never trust, always verify" mindset. Every access request is authenticated and authorized in real-time, considering factors like the user's identity, device type, location, and the device's security status. This framework builds on earlier steps, such as monitoring and securing the supply chain, to further strengthen your network's defenses.
4.1. Use Machine Learning for Threat Prevention
Machine learning (ML) offers a powerful way to enhance threat detection in real-time. By analyzing user activity, device logs, and network traffic, ML systems can identify unusual patterns - like a user attempting to access sensitive data from an unexpected location or a device displaying abnormal communication behavior.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on known malware signatures, ML-based tools can identify zero-day threats by recognizing suspicious behavior patterns. These systems can also perform Layer 7 inspection, analyzing application-level content to block specific actions, such as unauthorized file transfers or access to restricted URLs.
For 5G networks supporting critical services like telemedicine or industrial automation, ML tools should monitor data at every stage - whether it's stored, in transit, or actively being processed. Additionally, configure these systems to detect "toxic combinations", where multiple vulnerabilities align to create exploitable attack paths. For example, an over-permissioned service account combined with exposed cloud storage could become a significant risk. These proactive measures set the stage for the identity-based controls discussed in the next section.
4.2. Apply Zero Trust Principles
Once automated threat detection is in place, the focus shifts to enforcing identity-based security measures. Permissions should be assigned based on user roles, applications, and contextual factors. To streamline authentication, integrate your Zero Trust framework with identity management systems like Active Directory, RADIUS, or LDAP.
Device posture needs to be continuously evaluated. This involves scanning devices for signs of malware, checking firewall configurations, and ensuring firmware is up to date. Devices that fail these checks should be automatically quarantined until they meet security standards.
Microsegmentation is another critical component. By dividing your network into isolated zones, you can prevent attackers from moving laterally across your infrastructure. This is especially important in 5G environments, where multiple virtual network functions often share the same infrastructure. Such segmentation protects customer resources and ensures that a breach in one area does not compromise the entire system.
4.3. Use NAC and Firmware Databases
To further strengthen your Zero Trust strategy, enforcing device-level security is essential. Network Access Control (NAC) systems play a key role by validating every device - whether it's a smartphone, IoT sensor, or industrial controller - before granting access. As Tom Barsi, President and CEO of ConSentry Networks, highlights:
"You can't control what you can't see. Visibility is crucial throughout the LAN security lifecycle."
NAC systems should also account for non-human identities, such as IoT devices or medical equipment. By using agentless scanning and behavioral analytics, these systems can monitor devices based on their activity patterns rather than relying solely on credentials. Maintaining up-to-date firmware databases is equally important. These databases track authorized versions and configurations, flagging any unauthorized changes to critical assets like container images or templates.
Post-admission monitoring completes the picture. Just because a device passes initial security checks doesn't mean it should be trusted indefinitely. Regularly audit all traffic associated with users and devices to quickly identify and respond to potential threats. Instead of disconnecting entire users, configure your systems to isolate compromised applications or transactions, ensuring business operations continue uninterrupted while containing the risk.
5. Working with Experts and Resources
Rolling out 5G networks is no walk in the park. The technology brings with it a host of challenges, including new vulnerabilities tied to cloud-native functions, edge computing, and vast IoT ecosystems. To navigate these complexities, building on secure supply chains and adopting Zero Trust principles is key. But there’s more - working with external experts can significantly strengthen your 5G security. As Kiran Gurudatt, Director of Cybersecurity at Capgemini, puts it:
"The complexity of such an ecosystem makes risk assessment an essential part of implementing security for 5G."
The right guidance and resources can make all the difference between a smooth, secure deployment and a costly security breach.
5.1. Work with Industry Advisors
When choosing advisors, make sure they align with established standards like NIST, ISA/IEC 62443, MITRE FiGHT, and 3GPP. These frameworks are critical for securing both the technical aspects - like endpoints, RAN, MEC, and network slicing - and operational areas such as governance, incident management, and personnel vetting.
Your advisors should be able to adapt their recommendations to fit your specific 5G setup, whether it’s Standalone (SA), non-standalone (NSA), or a hybrid configuration. Lakshmi Kandadai from Palo Alto Networks underscores this point:
"A Zero Trust ecosystem is the best way to ensure consistent enforcement of security policies across an enterprise 5G network."
Look for advisors with a proven track record in managing edge clouds and private networks, and who emphasize Zero Trust principles. They should also have strategies for securing your supply chain, including evaluating multiple suppliers and business partners.
For instance, in March 2025, Palindrome Technologies conducted a security assessment for a private 5G Standalone network geared toward industrial automation. By identifying 30 attack vectors and addressing vulnerabilities, they reduced the client’s attack surface by 75%, all while ensuring real-time performance and reliability in a high-demand industrial setting.
Certifications matter too. Advisors should guide you through audits and certifications for industry standards like IEC 62443, covering security levels SL1 through SL3. And instead of one-off assessments, prioritize continuous monitoring and anomaly detection systems. This is especially crucial as 98% of IoT traffic remains unencrypted, making ongoing visibility a must.
Pairing expert advice with advanced tools can streamline the evaluation process for vendors and partners.
5.2. Use AI Tools and Business Directories
AI tools and business directories can simplify the process of identifying vendors, assessing risks, and refining deployment strategies. Platforms like The B2B Ecosystem offer directories for vetting potential partners before you sign on the dotted line. As Bob Moore, CEO of Crossbeam, highlights:
"Your place in an ecosystem of tech partners is just as important, if not moreso, than the quality of your product itself."
Business directories give you insights into a partner’s ecosystem - its size, scope, and maturity - helping you avoid partnerships that don’t deliver value. Before committing, ensure potential vendors have the resources and program maturity needed for co-marketing and technical collaboration. This prevents uneven workloads and unmet expectations.
AI tools can also play a vital role in pinpointing vulnerabilities within 5G system architectures and supply chains, which are common attack targets. Tools like Risk Analyzer and AI Process Optimizer from The B2B Ecosystem can automate risk scoring based on financial and market data, while also helping modernize outdated processes to meet 5G demands.
Creating an Ideal Partner Profile (IPP) can help you evaluate potential vendors based on factors like budget, leadership support, and ecosystem influence. This structured approach ensures you’re teaming up with organizations that align with your goals. Additionally, guides on securing 5G cloud infrastructures offer practical methods to prevent lateral movement and contain breaches.
Combining expert advisors with advanced tools gives you a strong edge. By partnering with established entities listed in directories, you not only benefit from their expertise but also tap into their networks and reputation. This is a huge advantage in the 5G space, where 75% of enterprise-generated data is expected to be created and processed at the network edge by 2025. Strong partnerships that span multiple technology domains will be essential to keeping pace with this rapid evolution.
Conclusion
Deploying 5G technology comes with its fair share of challenges, especially when it comes to addressing vulnerabilities that could put your entire operation at risk. Experts stress the importance of embedding strong cybersecurity measures right from the design phase - a "security-by-design" approach that's simply not optional. By managing risks early, you not only safeguard your business but also protect the billions of IoT devices that will rely on your network. This proactive mindset helps tackle critical threats, from counterfeit components to vulnerabilities in edge computing. With 5G networks becoming prime targets for cybercriminals and foreign adversaries, staying ahead of potential threats is a must.
The checklist we discussed earlier strengthens every step of your 5G rollout. From securing your supply chain to adopting Zero Trust principles and implementing continuous monitoring, these steps ensure a robust defense. Considering only 21% of businesses report having highly resilient networks today, there’s a clear need to prioritize these strategies.
Collaboration between the government and private sectors also plays a key role in bolstering 5G security. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices is vital. Platforms like The B2B Ecosystem offer valuable resources, including directories and AI tools, to help with vendor selection and risk evaluation. These collective efforts create a stronger security framework across your network. As 5G transforms critical infrastructure, from manufacturing to cloud operations, integrating these measures early ensures your operations remain secure while enabling growth.
FAQs
What are the key security risks businesses face when deploying 5G networks?
The rollout of 5G networks brings with it a host of new security challenges for businesses. One of the most pressing issues stems from the supply chain. Hardware, software, and services sourced from untrusted vendors can introduce risks such as malicious code, counterfeit parts, or poorly designed components that could jeopardize network security and data integrity. On top of that, the broader infrastructure required for 5G significantly increases the attack surface, providing adversaries with more opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities if proper safeguards aren't in place.
The software-defined nature of 5G networks adds another layer of complexity. Since these networks rely on general-purpose operating systems, they become vulnerable to common IT threats like malware or unauthorized code execution. Compounding the problem, 5G’s highly distributed architecture reduces the effectiveness of traditional physical security checkpoints, making it easier for harmful traffic to infiltrate and spread. Additionally, legacy vulnerabilities carried over from 4G LTE systems, along with flaws in standards or proprietary implementations, further heighten the risks.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach. Businesses can minimize threats by rigorously auditing their vendors, adopting zero-trust network architectures, and continuously monitoring software components for vulnerabilities. The B2B Ecosystem provides valuable tools and guidance to help organizations navigate these complexities and enhance their 5G security measures.
How does adopting Zero Trust improve 5G network security?
Zero Trust operates on a simple yet powerful principle: never trust, always verify. It’s a game-changer for 5G network security, where every device, user, and service request undergoes constant verification. With 5G's software-driven and cloud-native design, the potential attack surface expands significantly, making identity-based access controls a necessity. These controls help block unauthorized access and restrict lateral movement within network slices.
By adopting Zero Trust methods like micro-segmentation and risk-based authentication, businesses can safeguard sensitive data, maintain uninterrupted services, and meet regulatory standards. For enterprises rolling out 5G, The B2B Ecosystem offers practical guidance on weaving Zero Trust into their strategies - covering everything from evaluating vendor risks to securing edge devices and cloud environments. This approach not only reduces vulnerabilities but also paves the way for 5G to drive innovation and business growth.
How can AI tools help reduce risks during 5G deployment?
AI tools are transforming how 5G networks are deployed by making network management smarter and more efficient. These tools can process massive amounts of data automatically, identifying potential issues like interference and fine-tuning network settings - such as channel selection or transmit power - without needing human input. This not only ensures stable connectivity but also minimizes errors that could lead to security problems or performance hiccups.
What’s more, AI delivers predictive insights by analyzing historical data to forecast network behavior. For instance, it can predict when a network might face capacity overloads and reallocate resources in real time to prevent service interruptions. This forward-thinking approach helps businesses sidestep costly downtime and maintain momentum during the demanding rollout of 5G.
The B2B Ecosystem’s AI tools take this a step further by offering analytics that pinpoint risks related to timelines, budgets, and collaboration among stakeholders. By weaving these insights into your deployment strategy, you can focus on what matters most, make faster decisions, and ensure your projects stay on budget and on schedule.


